Practical Virtual Reality and its Growing Uses for Web
There is more and more talk about virtual reality as a practical tool. In many areas, virtual and augmented reality has become an indispensable tool for solving complex tasks. For example, in medicine to practice surgery, in design to create car models, in construction to visualise projects, etc.
The growing trend is to take advantage of VR opportunities on the web as well. Let's find out what the advantages of VR on the web are and why you should think about VR web applications today.
Virtual reality as a practical tool
In recent years, a number of innovative industries have adopted virtual reality as a practical tool, not just for experimenting, but as a full-fledged tool similar to a laptop or a mobile phone.
Implementing virtual reality in this way also creates exciting new job opportunities and speeds up many processes that would have taken a huge amount of energy and time in the past.
Staff training and specialists
Many in the field have already implemented virtual reality for the purposes of training their employees quickly and in a risk-free manner and many are in the process of implementing similar solutions. The areas that benefit most from such training programs are, for example, medicine, construction and national defense.
Surgeons can practise difficult surgeries at the simulated operating table; technicians can install equipment on virtual mobile masts; the military can simulate and play through complex battle scenarios.
Medicine and health
With the help of virtual reality, it is possible to simulate all sorts of different situations that can be used to train medical staff. From the fact that surgeons can practise complex surgeries to the fact that workers in different medical fields can play through potential situations that may arise, like the emergency room or disaster scenarios.
The use of virtual reality has become more popular in both physical and mental health therapy as well. For example, VR applications have been found to help relieve pain in patients with severe burns. In physiotherapy, VR helps the patient make precise movements so that the doctor can monitor and analyse the progress of the work done.
Education
Virtual reality has the wonderful ability to be of great help to storytellers by adding in the opportunity to experience all kinds of interactive scenarios. In the school education landscape, virtual reality has applications in almost every field.
In classrooms equipped with VR headsets, it is possible to experience historical events for yourself or to learn complex concepts of chemistry, physics or biology in an interactive environment. Additionally, several galleries already use VR tours of their exhibitions, which have become especially relevant in connection with COVID-19.
We also have an example from the Estonian Museum of Natural History’s bat exhibition, where a VR space has been set up to get to know the small creature.
The “Hirmus Armas Nahkhiir” exhibition is enriched by Oculus Go headsets, which allow you to watch the bats' lives up close and take a flight through the eyes of the creature.
Manufacturing
VR has been an important tool for engineers for some time now, helping them to view, simulate, and manipulate models of mechanisms where physical prototyping would make work slower and more complex. Working in this way helps keep costs much lower compared to physical prototyping.
Design and architecture
Designers, artists and architects are increasingly adopting virtual reality for their purposes as well. For example, VR allows you to design concepts for future cars or houses in the free space around you.
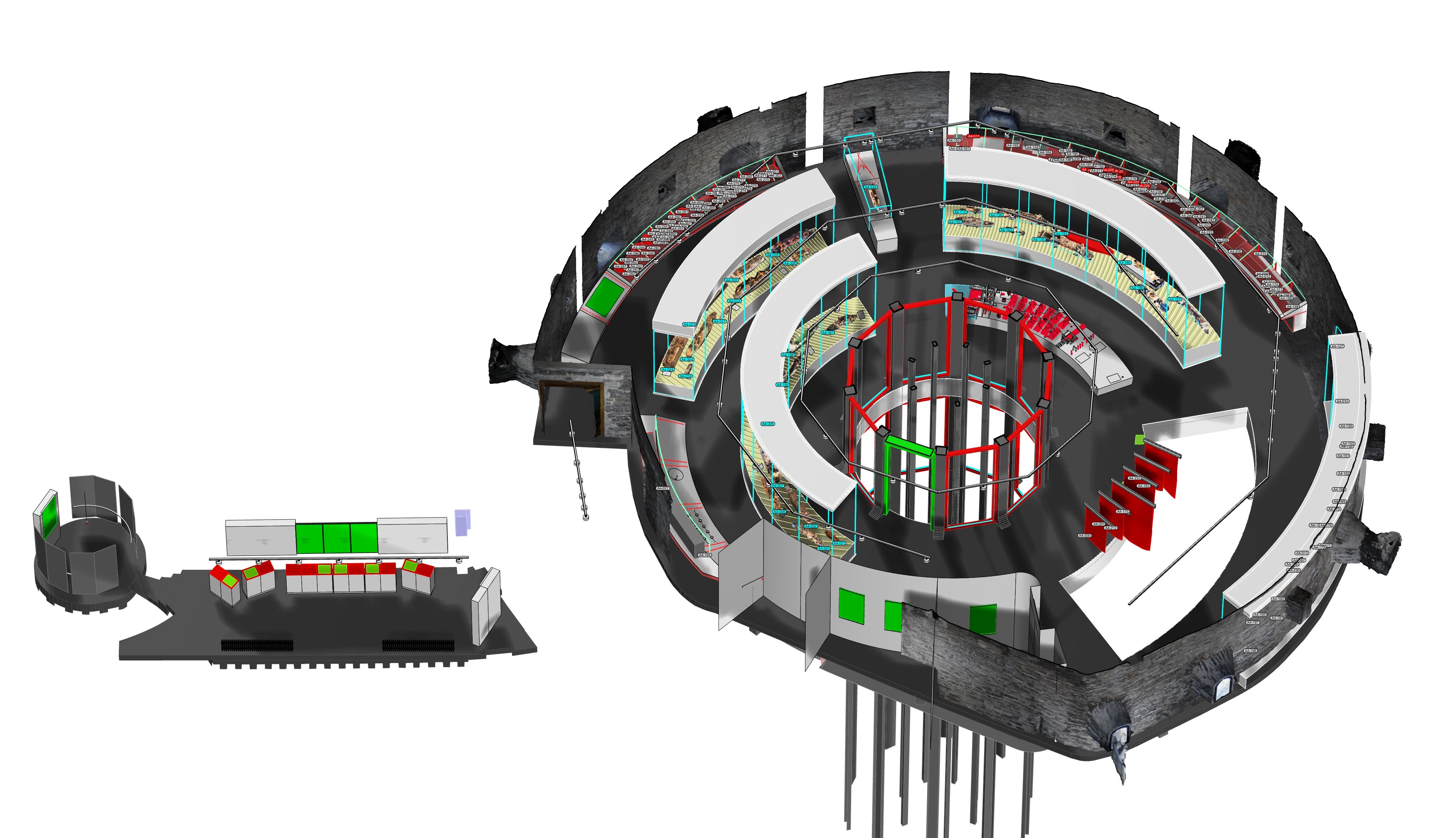
In Estonia for example, virtual reality was used in the development of the recent Fat Margaret’s project to plan out the space, demonstrate it to the client and plan the setup of the exhibitions before construction even began.
Architect Artur Staškevitš (Inphysica) sent us some pictures of how the museum rooms were visualized during the work.
The rise of VR on the web
The use of virtual reality on websites has become increasingly popular. Just as it’s natural with the modern web to be able to view a page on a phone, tablet, or large screen, so is enabling VR for virtual tours, product promotions, or other 3D-enabled components becoming more relevant as well.
Although there are still relatively few VR headsets in use (171M VR users worldwide according to a 2018 survey, it can be expected that the market will expand and VR devices will become more mainstream in the coming years.
Demand for stand-alone VR headsets is projected to increase 16-fold between 2018 and 2022 . Demand has also been boosted by the COVID-19 crisis, which has been a major springboard for VR technology. In the near future, various augmented reality glasses will also be launched on the market, which will further expand the market opportunities.
Why offer VR capability on your web today?
The web-based VR experience has several advantages over application-based solutions. For example:
- Possibility of integrating VR into the content of the page. Imagine a situation where a 3D model of a product - for example, a speedboat - is displayed in the header of a page when viewed from a computer. It is also possible to display this model in VR and add components that make the VR experience a virtual product presentation. Such a VR component could also be successfully used by the company at trade fairs, trainings and other places where it is necessary to introduce the product.
- There are multiple VR components that can be displayed on a page. Let’s say that, for example, the company has several speedboats. There may be a different introductory tour for each vessel. Such tours can also be made universally usable, which means that the tours can be viewed equally well on a mobile phone, tablet, computer screen, TV, and also in virtual reality by using the main unit available to you.
- The pages used by the VR component are easy to share using a web address. Each product with a virtual tour can be easily shared, just like any other website.
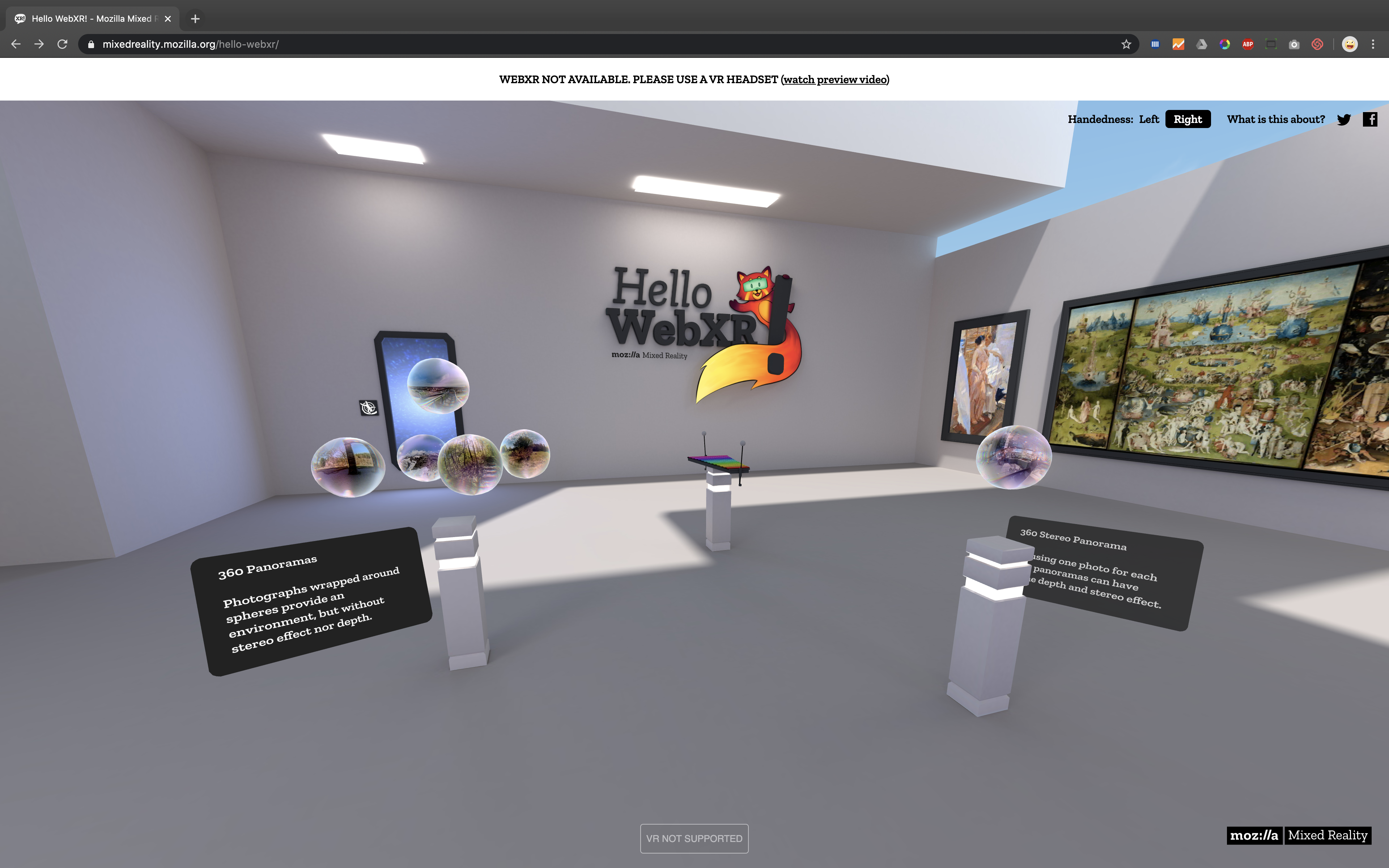
Here you can see an example of Mozilla WebXR that works in both the browser and on VR headsets.
However, there are some points that need to be taken into consideration when using VR online in order to achieve the best user experience. For example:
- The web components cannot be set up with very complex geometry. The more complex the model or animation, the heavier the VR component of the web will be, which means longer loading times for the user. Complex models can be replaced with, for example, 360 photos or videos. However, as the performance of different devices increases across time, then this is only a short-term problem.
- A web application that is universally usable must be optimised for the weakest devices, such as mobile devices. This means that you should avoid real-time effects and very complex interactions and animations that demand a lot from the device.
Examples of using virtual reality on the web
Here are some exciting examples of how virtual reality can be used on the web.
To promote products
City24 virtual tours
City24 has introduced a virtual tour solution that allows the user to navigate through a 3D-scanned space. This is a good example of how a VR-capable web application can be used equally well on all devices.
To promote tourism
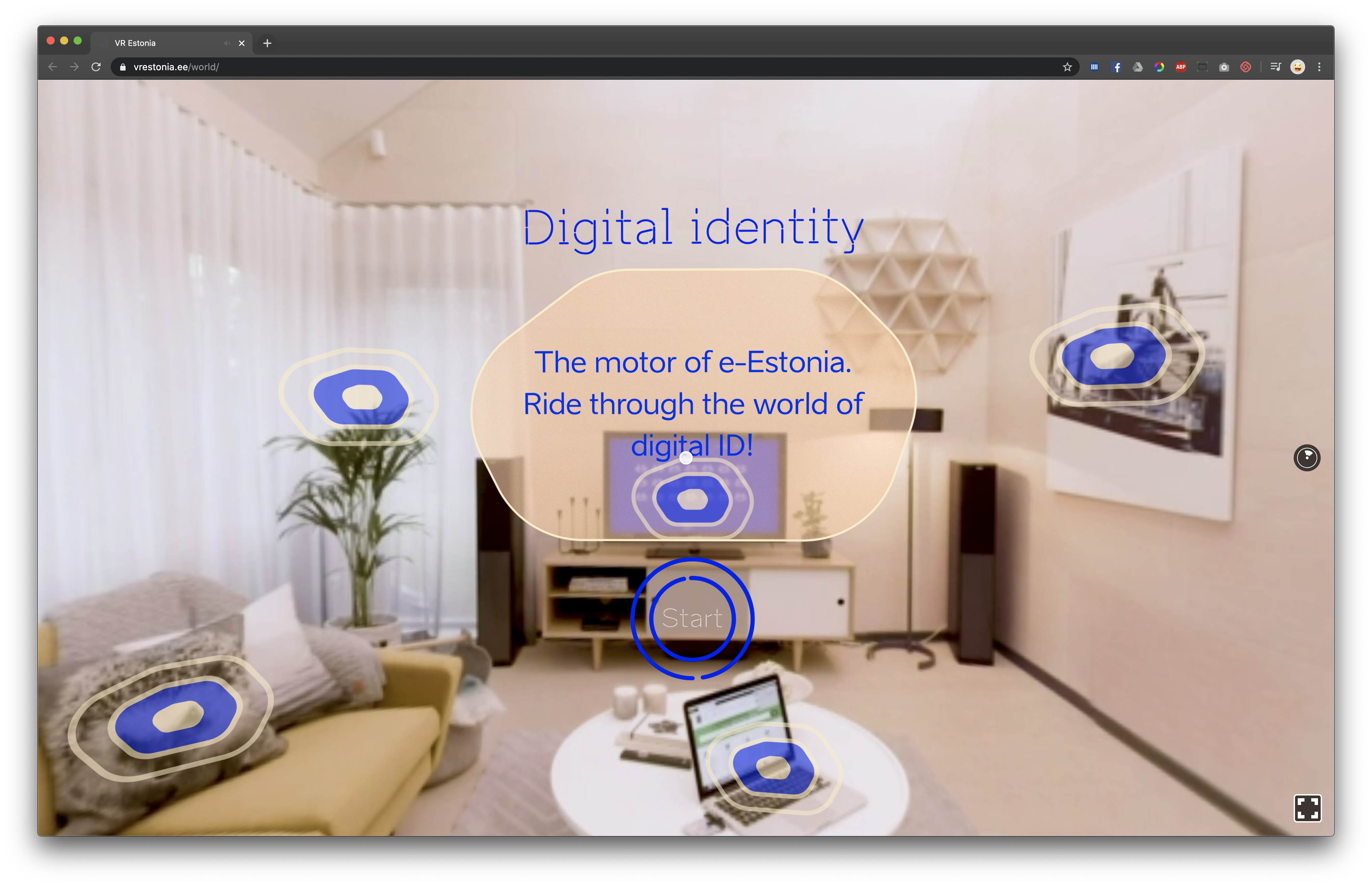
One part of the E-Estonia page is a virtual tour that introduces Estonia as a digital country. The tour consists of 360 panoramic photos and videos that the user can navigate between to listen to various presentations, each connected to their respective media file. The solution can also be used on devices other than VR headsets.
To promote education
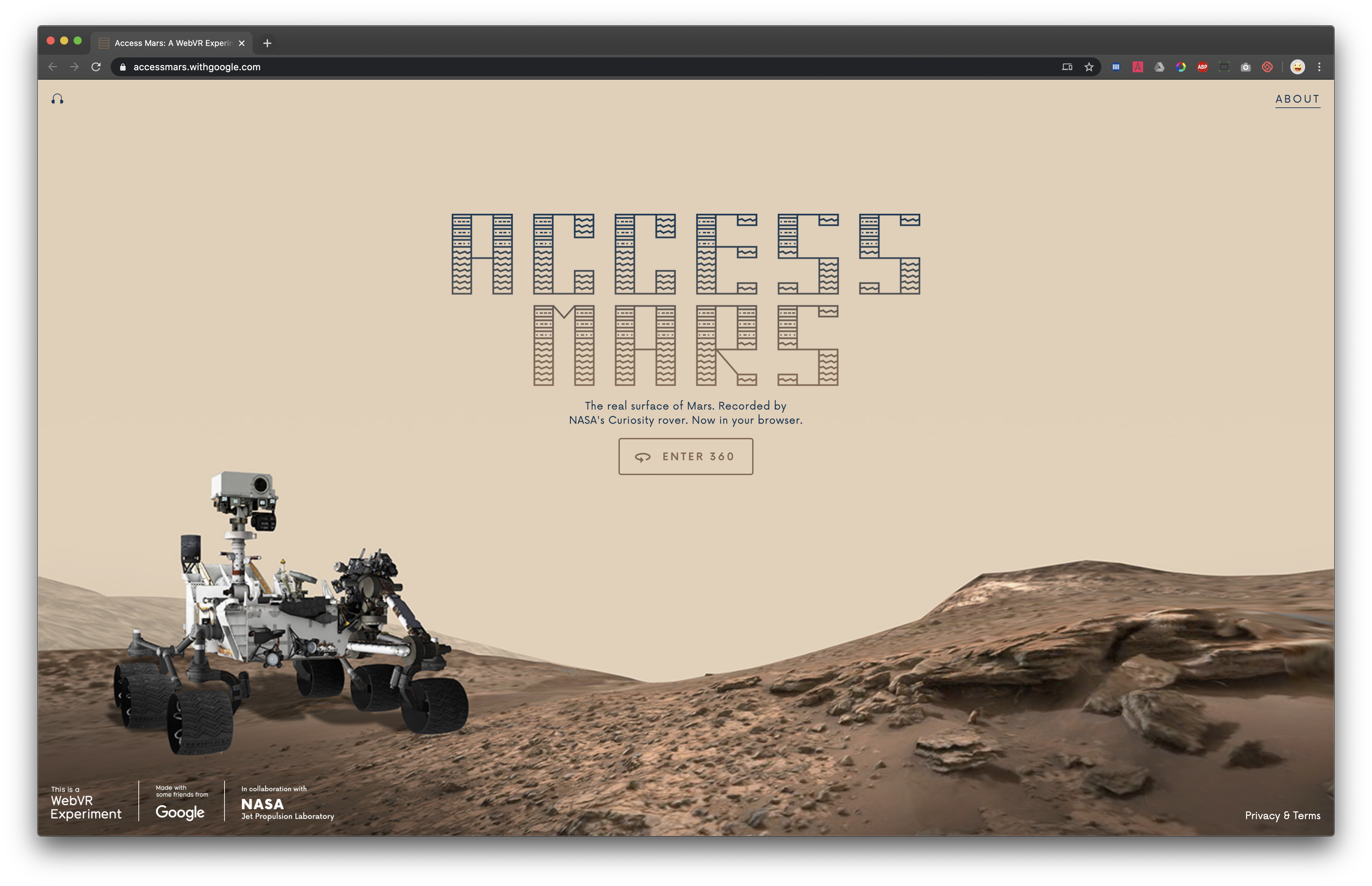
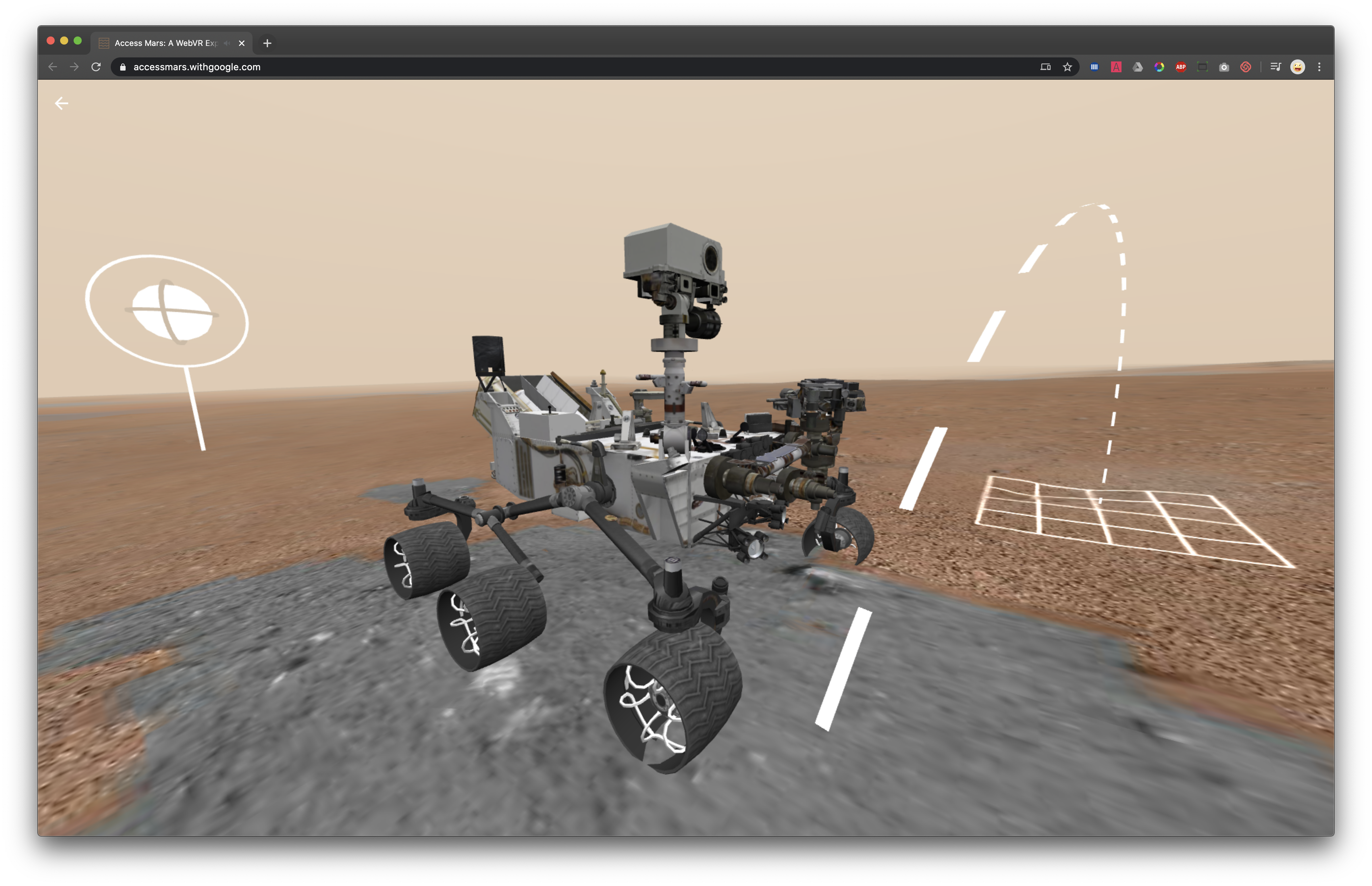
NASA and Google have partnered up to create an interactive web application for exploring the Curiosity Mars rover. The application uses photographs taken by the rover and topographic information to create an environment for the user to walk around in. Additionally, it is possible to get acquainted with different parts of the rover yourself.
Conclusion
The field of virtual reality is still in its infancy, but in some industries, serious VR tools are already being used. Augmented and mixed reality technologies also creep closer to creating a screen-free work environment which would change the nature of web consumption. Currently, VR components on the web are still limited in use, but the use cases mentioned above are already quite real. I hope this blog post can help you think about how virtual reality can enrich your website in the future.